If you are familiar with LTE then it will be easy for you to understand gNB, AMF, UPF, SMF functions in 5G. In fact at the high level LTE eNB and 5g gNB have same functionalities. Since we are going to have 5g core, therefore protocols are going to change like Mac scheduling etc. In 5G most of the changes are being done at phy layer because 5G will be using mmwave. Please go through millimeter wave by clicking here.
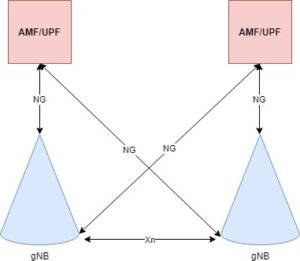
gNB, AMF, UPF, SMF functions in 5G 5G Radio Network
gNB Functions in 5G:
These are some high level functions of 5g gNB from 3gpp release 15:
- gNB does Radio Resource Management such as Radio Bearer Control, Radio Admission Control, Connection Mobility Control.
- Mac scheduling: Dynamic allocation of resources to UEs in both uplink and downlink.
- gNB does the IP header compression, encryption and integrity protection of data.
- gNB selects AMF for UE during attach process. If a UE already has an AMF information, then it routes the request to the AMF.
- It Routes User Plane data towards UPF(s).
- Routing of Control Plane information towards AMF.
- Connection setup and release.
- Scheduling and transmission of paging messages.
- Scheduling and transmission of system broadcast information (originated from the AMF or O&M).
- Measurement and measurement reporting configuration for mobility and scheduling.
- gNB does transport level packet marking in the up-link.
- Session Management.
- Support of Network Slicing.
- QoS Flow management and mapping to data radio bearers.
- Support of UEs in RRC INACTIVE state.
- Distribution function for NAS messages.
- Radio access network sharing.
- Dual Connectivity.
- Tight inter-working between NR and E UTRA.
AMF Functions in 5G:
In LTE, we have MME. But in 5G we have AMF (access and mobility management functions). AMF is kind of master node in 5g core and It has lot of functions to do.
The AMF performs the following main functions:
- The Non-Access Stratum (NAS) signalling termination.
- The NAS signalling security.
- The Access Stratum (AS) Security control.
- Inter CN node signalling for mobility between 3GPP access networks.
- Idle mode UE Reachability (including control and execution of paging re transmission).
- Registration Area management.
- Support of intra-system and inter-system mobility.
- Access Authentication.
- Access Authorization including check of roaming rights.
- Mobility management control (subscription and policies).
- Support of Network Slicing.
- SMF selection.
UPF Functions in 5G:
Again in 5G, there will be no SGW (Serving Gateway). So, Here we have UPF (User Plane Function).
The UPF will perform the following main functions:
- Anchor point for Intra/Inter-RAT mobility (when applicable).
- External PDU session point of interconnect to Data Network.
- Packet routing & forwarding.
- Packet inspection and User plane part of Policy rule enforcement.
- Traffic usage reporting.
- Uplink classifier to support routing traffic flows to a data network.
- Branching point to support multi-homed PDU session.
- QoS handling for user plane, e.g. packet filtering, gating, UL or DL rate enforcement.
- Uplink Traffic verification (SDF to QoS flow mapping).
- Downlink packet buffering and downlink data notification triggering.
SMF Functions in 5G:
There will be no PND in 5G. So, All IP allocations and session management will be done by SMF (Session Management Function).
The SMF will perform the following main functions:
- Session Management.
- UE IP address allocation and management.
- Selection and control of UP function.
- Configures traffic steering at UPF to route traffic to proper destination.
- Control part of policy enforcement and QoS.
- Downlink Data Notification.
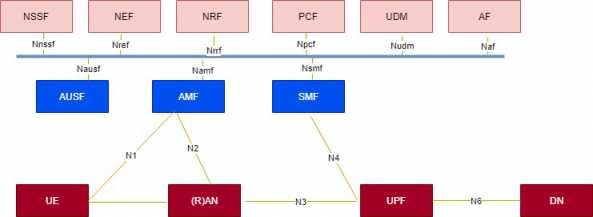
Read 5G architecture to understand better. 5G system Architecture: Service based and reference point architecture.
External source 3gpp release 15.


very good document