All the architectures in this article are based on 3gpp release 15 and we will discuss 5G system Architecture here.
Service Based Architecture
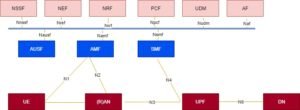
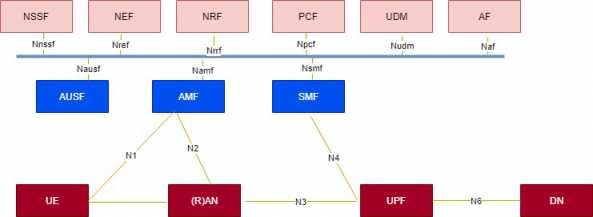
Below is the non roaming reference 5G system architecture. Service based interfaces are there within the Control Plane.
This architecture is from spec 23.501.
The 5GC architecture definition uses a so called Service Based Architecture (SBA) framework, where the architecture elements are defined in terms of Network Functions (NFs) rather than by traditional Network Entities.
All the network functions communicate to each other via common interface. So, through this common interface a network function provides services to other authorized network function.
The 5G System is composed of:
- The User Equipment (UE).
- The Radio Access Network.
- The User Plane Function (UPF) which handles the user data.
- The Application Function (AF) which handles the applications.
- The external Data Network (DN).
- The other NFs (NSSF, AMF, etc.).
Basic Network Functions
NRF: The Network Repository Function provides support for NF services management including registration, deregistration, authorization and discovery.
NEF: The Network Exposure Function provides external exposure of the capabilities of the network functions. External exposure can be categorized as Monitoring capability, Provisioning capability, Application influence of traffic routing and Policy and Charging capability.
UDM: The Unified Data Management the 5GC supports Data Storage architecture for Compute and Storage separation. Basically, the Unified Data Repository (UDR) is the master database.
UDSF: The Unstructured Data Storage Function will store dynamic state data.
NSSF: Network Slice Selection Function selects network slice for users based on services.
AMF: The Access and Mobility management Function in charge of the signalling like mobility, security etc. Since the AMF support UEs with different mobility management needs. Thus, whenever required, mobility can be hidden from the application layer to avoid interruptions in service delivery.
SMF: The Session Management Function in charge of the signalling related to User Data traffic like session establishment, etc.. So, together with the AMF, the SMF can be support customized mobility management schemes such as Mobile Initiated Connection Only (MICO) or RAN enhancements like RRC Inactive state.
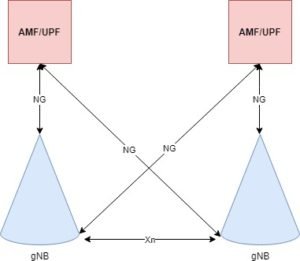
5G Architecture in Reference Point Representation
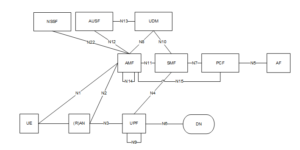
This figure depicts the 5G System architecture in the non-roaming case. This is the reference point representation which shows that how various network functions interact with each other.
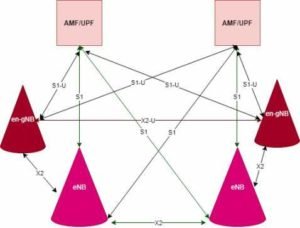
Standalone Architecture.
In case of standalone, 5g base station will connect to 5g core. So, there will be a new ran and a new next generation core. Standalone is the full feature 5G. Thus, this will take time to become reality. Since, most of the network providers are going to launch non standalone version of 5g. So, according to experts standalone will be available may be by 2020 in some parts of the world.
Non-Standalone Architecture.
In case of non standalone, 5G RAN will be there within LTE network. So, there is no next generation 5G core in this scenario. Thus, this will be initial deployment by most of the network provider. Some of the network providers has started testing this feature but the real problem is that there is no 5G mobile device available in the market. Qualcomm and other companies are working hard to launch their 5G chip set.
To know more about standalone and non-standalone click here.
For more topics on 5G and 5G network please visit 5G important topics.
3gpp 23.501 specs link 3gpp.