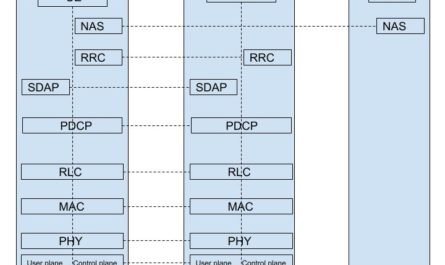
5G Physical Layer Overview
If you have little bit understanding of LTE physical layer then it will be easy to understand 5G physical layer.
Numerologies
Definition from Wikipedia: Numerology is any belief in the divine, mystical relationship between a number and one or more coinciding events. It is also the study of the numerical value of the letters in words, names and ideas. It is often associated with the paranormal, alongside astrology and similar divinatory arts.
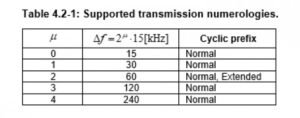
In 5G also the meaning is same. If you see the below table from technical specification 38.211, 5G supports 5 types of cyclic prefixes.
Cyclic prefix in 5G
5G supports 5 types of Subcarrier spacing and cyclic prefix. Accept numerology 2 i.e subcarrier spacing 60 kHz all are normal cyclic prefix. Cyclic prefix 6o kHz supports normal as well as extended.
Waveform
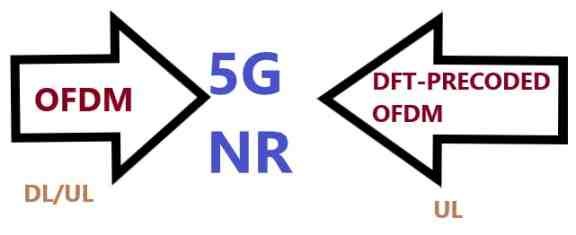
Downlink (DL) waveform uses OFDM with CP just like LTE. But opposit to LTE, OFDM can also be used in the NR uplink (UL) direction. As a complement, DFT-s-OFDM (OFDM with DFT precoding) can be used in the uplink although limited to single-layer transmission only.
As we all know 5G will be supporting various deployment scenarios and wide range of carrier frequencies.Because of this, NR will support multiple subcarrier spacings. Basically 15kHz, 30kHz, and 60kHz subcarrier spacing can be used for network deployments operating in frequency bands below 6 GHz, referred to as frequency range 1 (FR1). For network deployments above 24 GHz 60 kHz and 120 kHz subcarrier spacing can be used. Frequencies above 24 GHz also know as frequency range 2 (FR2).
Frame Structure of 5g Physical Layer

Frame in 5G
Similar to LTE, downlink and uplink transmissions are organized into frames with frame duration = 10 ms.
Sub-frame in 5G
Each frame consists of 10 sub-frame as shown above in the picture. Therefore each sub frame duration is 1 ms.
Slot in 5g
Each slot consists of 14 OFDM symbols for normal cyclic prefix and 12 OFDM symbols for extended cyclic prefix.
The below table will give you relation between symbols, slots and frame.
In the time domain, a subframe of 1ms consists of a number of slots. Each slot has a length 14 symbols. Therefore the length, in ms, of a slot and also the number of slots per subframe depends on the numerology.
When u = 0 i.e sub carrier spacing is 15 kHz
Number of symbols per slot = 14, number of slot per frame is (2 power 0)*10 =10 and number of slot per subframe is 2(power 0) = 1.
When u = 2 i.e sub carrier spacing is 60 kHz
Number of symbols per slot = 14, number of slot per frame is (2 power 2)*10 =40 and number of slot per subframe is 2(power 2) = 4.
When u = 4 i.e sub carrier spacing is 240 kHz
Number of symbols per slot = 14, number of slot per frame is (2 power 4)*10 =160 and number of slot per subframe is 2(power 4) = 16.

When u = 2 i.e sub carrier spacing is 60 kHz (Extended cyclic prefix)
Number of symbols per slot = 12, number of slot per frame is (2 power 2)*10 =40 and number of slot per subframe is 2(power 2) = 4.
![]()
You just need to remember numerology and calculate anything in above table.
NR supports both FDD and TDD operation with the same frame structure. In case of TDD, the direction of each OFDM symbol in a slot can be downlink or uplink for flexible traffic adaptation. The transmission direction can be semi-statically configured or dynamically changes as part of the scheduling decision. Furthermore, transmissions can be carried out over only a fraction of a slot with the minimum transmission consisting of only two symbols. Such very short transmissions mainly targets usage cases requiring low latency, such as some URLLC services.
Resource elements
The underlying data carrier for an LTE frame is the resource element (RE). The resource element, which is 1 subcarrier x 1 symbol, is the smallest discrete part of the frame and contains a single complex value representing data from a physical channel or signal.
and is uniquely identified by (k, l) where is the index in the frequency domain and refers to the symbol position in the time domain relative to some reference point. Resource element corresponds to a physical resource and the complex value
Resource Block
A resource block (RB) is the smallest unit of resources that can be allocated to a user. One resource block (RB) is defined as consecutive twelve subcarriers in frequency domain and 14 symbols i.e one slot in time domain